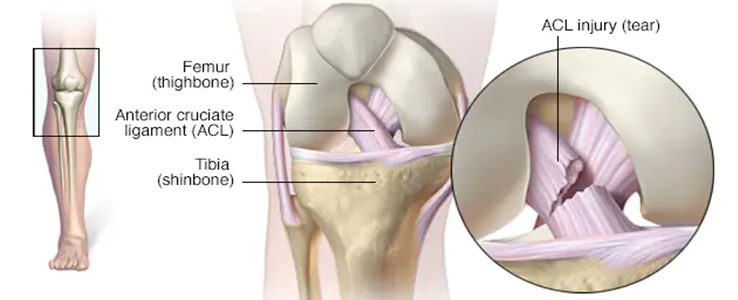
ACL (Anterior Cruciate Ligament) Injury -
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) rupture is one of the most
prevalent knee injuries among young people..
- An ACL injury happens when the ligament tears or ruptures, usually as a consequence of
a
violent twisting or pivoting action.
- This is frequent among athletes who compete in sports that involve fast changes of
direction, such as soccer, basketball, and football.
- However, these injuries can develop during normal activities or as a result of a severe
occurrence.
- ACL damage can cause knee discomfort and instability, making it difficult to walk or
participate in other activities.
- It can compromise the mobility and function of the knee.
- ACL damage can cause knee discomfort, swelling, instability, and trouble walking.
- In certain circumstances, a "pop" or "snap" may be felt during the injury.
Diagnosis
A comprehensive examination by a medical practitioner is required to
identify an ACL injury and evaluate the degree of the damage. This may include a physical
examination, X-rays, an MRI, or other imaging tests.
Treatment -
Treatment for an ACL injury varies according to the degree of the damage, the
patient's age, and the level of activity.
Conservative care of small ACL injuries, including physical therapy,
rehabilitation
exercises, and the use of assistive devices such as crutches or a brace, may be sufficient
to
relieve symptoms and restore knee function.
In more serious situations, surgical surgery (ACL repair) or rebuilding of the
ACL
may be required. The ACL restoration procedure generally involves replacing the injured ACL
with
a tissue transplant and restoring knee stability.
The rehabilitation phase following ACL damage or surgery is an essential part of
healing. Physical therapy and rehabilitation activities are necessary for restoring knee
strength, flexibility, and stability.
With correct diagnosis and treatment, the symptoms of ACL damage can be managed
and
full knee function restored. Physical therapy and rehabilitation are essential for achieving
a
satisfactory result, whether through conservative care or surgery.